Library and Learning Services
What is a systematic review?
A systematic review is a specialised literature review that tries to identify, appraise, select and synthesise all high-quality research evidence relevant to a research question. To get an overview, you can watch a recording of our training session Introduction to Systematic and Evidence Synthesis Reviews [November 2025, login required]. Below we layout some key aspects of the process.
How is it different to a literature review?
| Literature review | Systematic review |
| Key articles on a topic or overview of a research area. | Type of research methodology. |
| Influenced by needs of the researcher. | Focused on a specific research question. |
| No protocol for the items to include in the review. | Protocol is provided stating inclusion & exclusion criteria. |
| Search using keywords or key concepts to find enough/appropriate material. | Comprehensive search conducted in a systematic way. |
| Explicit and replicable search strategy. |
The process of conducting a systematic review
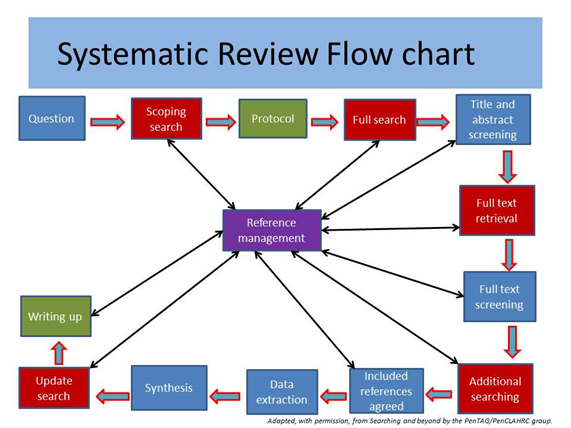
The key steps to follow:
- Formulate review question.
- Check your review is viable (trial/scoping searches).
- Write protocol including defined inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Develop a systematic search strategy, that can be reproduced across databases.
- Title/Abstract screening based on your inclusion criteria.
- Full text screening based on your inclusion and quality assessment criteria.
- Additional searching (e.g. citation searching, references, grey literature).
- The review team agree which studies to include in final review.
- Extract data or analyse studies.
- Write up and publish.
Traditionally, systematic reviews have been done in medicine and health, as a meta-synthesis using quantitative data. However, systematic reviews are now done in a variety of fields and the analysis might also be qualitative or mixed methods.
Find out more
- What are systematic reviews? Video from Cochrane.
- Introduction to Conducting Systematic Reviews Module from Cochrane Interactive Learning (note: this module is free, but you need to create an account to access it).
- Our Systematic Review Reading List has further resources on conducting systematic (and related) reviews.